PRACTICE 1: Reflective entry 1: Discuss how you are addressing the context of different audiences (local, national and/or international) and their perspectives for your inquiry.
Parker. P (n.d)
We are not just here to teach content. I am forever trying to instill in my students, the need to understand that we are also teaching skills and how to develop meaningful relationships to ensure they are fully functioning members of society when they leave. At secondary school, this is definitely the case. Tony Wagner states "I see schools that are succeeding at making adequate yearly progress but failing our students. Increasingly, there is only one curriculum: test prep. "(p 24).
Through my inquiry I am looking at the 21 century skill of critical thinking which is one of the seven survival skills he talks about to be able to survive in the new working world.
The Our Code, Our Standards, best summaries who the audience, we need to focus on, is:
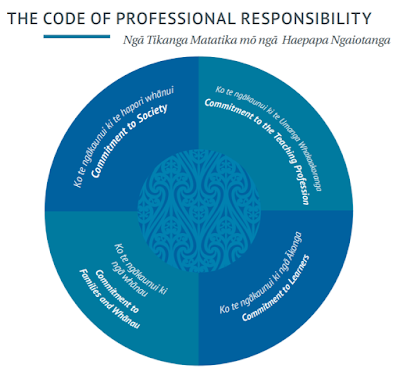 |
| Education Council (2017, p8) |
- Learners/Akonga - what are they taking out of this? How will it impact on them? What does critical thinking actually mean to them and how do you teach it? Year 10 students are notorious for being offtask and 'slacking around'. This has been the case for a number of years, we have to look at addressing this so that they are equipped to head into NCEA and apply the content knowledge they do have to any scenaro they are given.
- Educators/Kaiako - many of the educators in my school have been teaching for a long time. They have their ways of teaching that work for them. BUT do they work for learners of today? Through the use of the new teaching standards and our own inquiry, we hope to change this perspective and develop a growth mindset; in both other educators and the learners.
- Families/Whanau - There is a huge expectation on teachers to prepare learners for life after school. Many of the whanau in our community have poor experiences of school which they pass on to their children. This often is in conflict with being able to best prepare our students. How do we overcome this? Building relationships with our community, with a focus on the fact that it is culturally diverse plays an important role.
- Local community - a large proportion of our student body do not leave and go off to university. Therefore we have to look at our community to see what skills and knowledge they value to enable us to best prepare our learners. This includes "fostering learners to be active participants in community life and engaged in issues important to the wellbeing of society", (Education Council, 2017, p 12).
 |
| Teach Learn Reflection (2013) |
Reflections
I would like to think I am continuously reflecting on my teaching. Always looking to see what is working and what needs further development. An essential part of this is building the relationships with both the learner and their whanau. We all need to work together for a common goal that is not just about credit harvesting for the potential immediate return, more about what the learner is going to get of the experience in a holistic manner. This is backed by a NZ Curriculum that has a focus more on key competencies and the skill of learning rather than the content itself. Alongside this sits the new Teaching Standards which in of themselves are more holistic and allow the teacher to work alongside the students in the learning process. Through the inquiry model of both the teacher and the learner, we should continue to make progress towards developing the 21st century skills - in the case of my inquiry - Critical Thinking.
References
Education Council. (2017). Our code, our standards. Retrieved from
https://educationcouncil.org.nz/sites/default/files/Our%20Code%20Our%20Standards%20web%20booklet%20FINAL.pdfWagner, T. (2008). Even our “best” schools are failing to prepare students for 21st-century careers and citizenship. Educational leadership. retreived from
https://www.sisd.net/cms/lib/tx01001452/centricity/domain/22/rigor_redefined.pdf
Images
Education Council. (2017) The code of professional Responsibility retreived from
https://educationcouncil.org.nz/sites/default/files/Our%20Code%20Our%20Standards%20web%20booklet%20FINAL.pdf
Teach Learn Reflection (2013) retrieved from
https://www.deviantart.com/shinryu76/art/Reflection-of-Education-382701139
Parker, P. (nd) Quote Fancy, retrieved from
https://quotefancy.com/quote/1510381/Parker-J-Palmer-Whoever-our-students-may-be-whatever-the-subject-we-teach-ultimately-we



